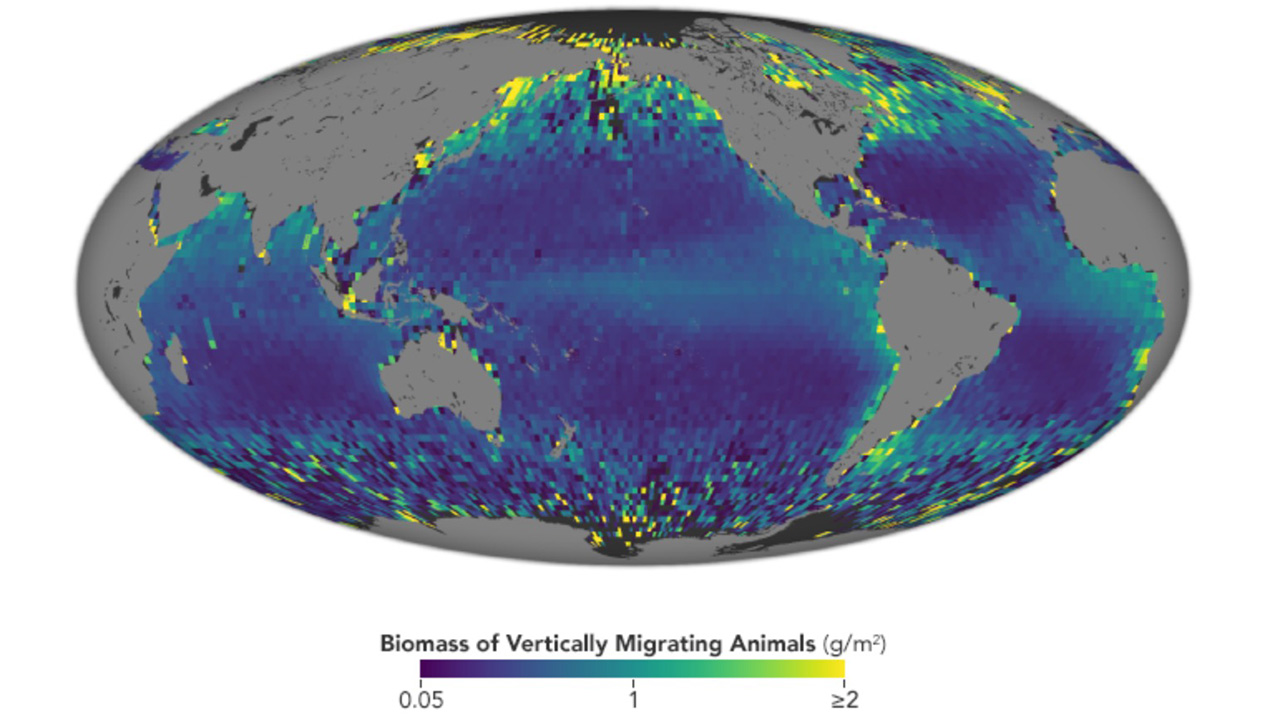
This natural daily movement has been observed from ships for decades though in limited areas and times. 5 rows Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.

Sustainability Free Full Text The Development Of An Efficiency Based Global Green Manufacturing Innovation Index An Input Oriented Dea Approach Html
Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals MJ Behrenfeld P Gaube A Della Penna RT Omalley WJ Burt Y Hu.
. Overview of attention for. Field Data. Satellite tags allow research of oceans twilight zone off Florida.
Ocean life allowing researchers to study diel vertical migration DVM at a global scale for the first time. Hostetler5 Philippe Tortell410 Scott C. Researchers from the University of Washington are using high-tech tags to record the movements of swordfish big deep-water migratory open-ocean fish that are poorly studied and get a window into the ocean depths they inhabit.
During WWII naval oceanographers discovered a reflective layer that rose and fell across their sonar screens once each day. Satellite-derived analysis of daily vertical migrations of ocean animals shows that the relative abundance and total biomass. Currently Associate Professor North Carolina State University Current Post-Docs.
First detected with sound new study monitors zooplankton movement with light. Like MODIS CALIPSO flies in the A-train constellation and has a 16-day repeat cycle Winker et al 2009 bp at 532 nm for the first vertical 225-m bin in the ocean Behrenfeld et al 2013. Behrenfeld1 Peter Gaube2 Alice Della Penna23 Robert T.
5 Burt4 Yongxiang Hu5 Paula Bontempi6 Deborah K. Awarded 2001 University of Austria Vienna Zooplankton vertical migration and POM transport in the Sargasso Sea. Lidar data new Home Standard Products Custom Products FAQ sheet.
Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals. Steinberg mainly investigates Oceanography Krill Euphausia Antarctic krill and Ecosystem. Vertical Motions and Their Effects on a Biogeochemical Tracer in a Cyclonic Structure Finely Observed in the Ligurian Sea.
Now researchers have observed it for a decade at the scale of entire gyres and basins of the ocean thanks to the Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations. Karen Stamieszkin Zooplankton pathways for carbon export NASA EXPORTS program. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.
The new ocean subsurface results eg Figure 7 from the ICESat-2 mission reveal high vertical resolution of subsurface ocean optical properties through the water column that are not available from passive ocean color records or from CALIOP active measurements. Since 2013 there have. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.
Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals. Nature 576 7786 257. Behrenfeld MJ 1 Gaube P 2 Della Penna A 2 OMalley RT 1 Burt WJ 3 Hu Y 4 Bontempi.
These results provide a detailed view of DVM activities globally and a path for refining the quantification of their biogeochemical importanceSatellite-derived analysis of daily vertical. The CALIPSO satellite was launched in 2006 with the primary goal of observing the vertical distribution of clouds and aerosols. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.
1 1 Satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of global ocean 2 animals 3 4 Michael J. 6 Siegel9 Chris A. It is considered the largest migration on Earth by total number of animals.
UW News Hannah Hickey. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals 18 citations In her most recent research the most cited papers focused on. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.
The potential for temporal mismatches is considerable in the ocean where daily light-dark cycles prompt diel vertical movements of numerous prey species. Mesoscale eddies influence the movements of mature female white sharks in the Gulf Stream and Sargasso Sea. These migrating animals on a global scale every 16 days for 10 years said lead author Mike Behrenfeld who is a senior.
Here marine mesopredators can optimize energy intake by foraging at night on prey closer to the ocean surface and ensure safety by resting at night when their predators visual acuity is. Further research revealed that it comprised swarms of fish and tiny sea creatures called zooplankton migrating toward the ocean surface as the sun set to feed. The ICESat-2 data thus provide a wealth of unique information to complement.
Measuring a large oceanic migration from space Each night marine organisms around the world migrate hundreds of meters to the surface to feed only to return once day breaks. Behrenfeld M J Gaube P Della Penna A OMalley R T Burt W J Hu Y Bontempi P S Steinberg D K Boss E S Siegel D A Hostetler C A Tortell P D and Doney S C 2019. Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals.
This cycle known as diel vertical migration DVM is thought primarily to be an adaptation to avoid predators near the sunlit surface and is responsible for transporting large amounts of nutrients. 25 February 2020 by. Nature 576 7786 257-261 2019.
Global satellite-observed daily vertical migrations of ocean animals Nature 2019.
Migration In The Ocean Twilight Zone

Evaluating The Potential Impacts Of The Diurnal Vertical Migration By Marine Organisms On Marine Biogeochemistry Aumont 2018 Global Biogeochemical Cycles Wiley Online Library

Whale Migrations How New Un Treaty Aims To Protect Species On The High Seas
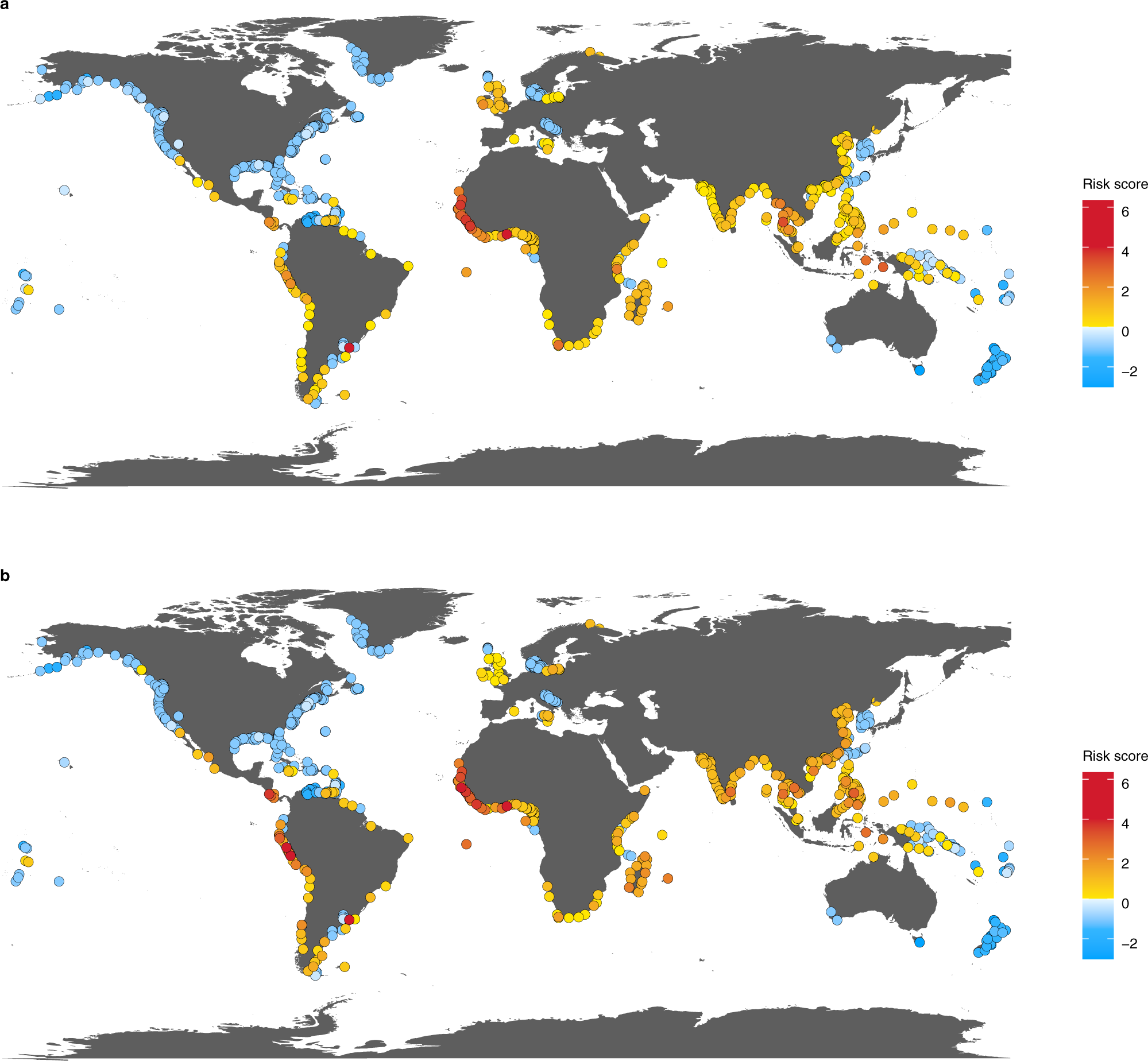
Revealing Global Risks Of Labor Abuse And Illegal Unreported And Unregulated Fishing Nature Communications

0 komentar
Posting Komentar